Showing posts with label technology and teaching. Show all posts
Showing posts with label technology and teaching. Show all posts
Monday, 14 March 2022
Sunday, 26 February 2017
TechnoTeachers are Entrepreneurs
The job of the teachers who try to integrate technology keeping pedagogical implications in mind is no less than entrepreneurs.
Their road is equally rocky filled with land mines.
This pilgrim's journey also passes through Slough of Despond, Hill Difficulty, Valley of Humiliation, Valley of the Shadow of Death, Doubting Castle, and the River of Death.
Such teachers have to fight to defeat teachers like Giant Despair, Giant Diffidence, Lord Hate-Good; and sometimes fight to win on their side people like , Obstinate, Mrs. Know-Nothing, Mrs. Bat's-Eye, Giant Maul, Mr. Fearing, Giant Slay-Good, Mr. Feeble-Mind and Mr. Ready-to-Halt.
TechnoTeachers, not only not only have to be self-motivated, but keep motivation level of most of other teachers, who are taking initial steps in using technology, high, hale and hearty.
As mentioned in this infographic, integrating technology is no less than entrepreneurship for teachers. Except for #2 , all these are golden rules for teachers who are willing to integrate technology. In #4, read *Students* instead of *investors*. #5 & #6 are imp. Keep sharing your innovative teaching practices on social media n do not get distracted by negative comments of people with crab mentality.
Saturday, 24 January 2015
Introduction to Education and Technology
Introduction to Education, Technology and ELT
This blog is based on the classroom discussion of the below given presentation, videos and images.
- Reading Resources:
Download from this blog post > search this English Language Teaching - 2 (Literature, Internet and English Language Teaching)
- Presentation 1: Education and Technology
Download from this blog post > search this English Language Teaching - 2 (Literature, Internet and English Language Teaching)
Introduction to Education and Technology from Dilip Barad
- Presentation 2: Teaching with Technology: Some Pedagogical Implications:
- Presentation 3: Web 2.0 Tools (View slide no. 25 to 37)
- Video - 1: Sir Ken Robinson: Changing Paradigm
- Video 2:Sugata Mitra: School in the cloud- SOLE
- Video 2:Sugata Mitra: School in the cloud- SOLE
- Video 3: Sugata Mitra: Future of Learning
- Video 4:Salman Khan: Let's use video to reinvent education
Video 5: Marc Prensky: Digital Natives, Digital Immigrants Video 6: David Crystal: The Effect of New Technologies on Engish: Video 7: David Crystal: The Biggest Challange for English Language Teachers in the times of Internet: Video 8: David Crystal: Texting is 'Good' for English Language - Image 1:
- Image 2:
- Image 3:
- Image 4: (Removed)
- Image 5:
- Image 6:
-
Image 7:

Image 7:
Quizzes:
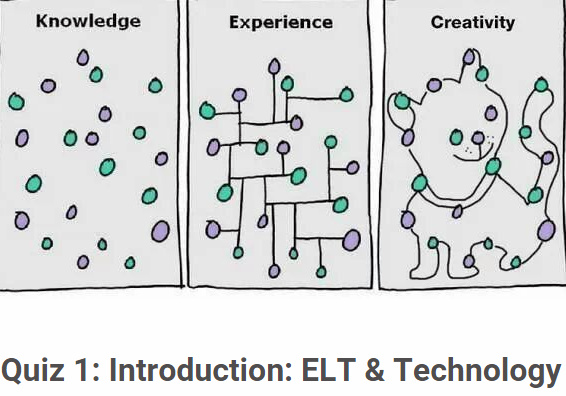
Quiz 1:
Labels:
David Crystal,
education and technology,
elt,
english,
Hall in the Wall,
ICT,
Ken Robinson,
Moodle,
Salman Khan,
SOLE,
Sugata Mitra,
technologies,
technology,
technology and teaching,
Unesco
Sunday, 28 December 2014
I.A. Richards: Figurative Language
The Figurative Language: I.A. Richards
Ivor Armstrong Richards – pioneer in the domain of New Criticism.
Ø His path breaking works: `
1. The Meaning of Meaning – 1923
2. The Principles of Literary Criticism – 1924
3. The Practical Criticism – 1929.
a. Four Kinds of Meaning
b. Two Uses of Language
c. On Simile, Metaphor and Symbol
1. To introduce a new kind of documentation to those who are interested in the contemporary state of culture whether as critics, philosophers, as teachers, as psychologists, or merely as curious persons.
2. To provide new technique for those who wish to discover for themselves what they think and feel about poetry (and cognate matters)and why they should like or dislike it.
3. To prepare the way for educational methods more efficient than those we use now in developing discrimination and the power to understand what we hear and read.
Ø His approach is pragmatic and empirical.
ü His experiment: Comments of students on poems without title and author. He gave suggestions, comments, interpretations and conclusions.
Ø His practical approach gave new path to literary criticism.
ü Instead of intuitive and impressionistic criticism, it became more factual & scientific.
ü He believed that poet writes to communicate, and language is the means of that communication. Language is made of words, and hence a study of words is all important if we are to understand the meaning of a work of art. Words carry four kinds of meaning: Sense, Feelings, Tone and Intention.
Ø The importance of context and rhythm &metre: the sound of the word invokes feeling. Rhythm, metre and meaning cannot be separated; they form together a single system. They are not separate entities but organically related. Therefore, a prose-paraphrase or an over-literal reading can never convey the total meaning of a poem.
Ø The nature of poetic truth
ü How do I. A. Richards differ from other New Critics?
Figurative Language: I.A.Richards
(A brief outline of Questions and Answers)
v What are the possible sources of misunderstanding in poetry?
v “How are we to explain to those who see nothing in poetical language but a tissue of ridiculous exaggerations, childish ‘fancies’, ignorant conceits and absurd symbolizations – in what way its sense is to be read?” explain with reference to the I.A.Richards’s essay The Figurative Language.
v “Poetry is different from prose and needs a different attitude for right understanding.” Elucidate.
v Critically evaluate I.A.Richards’s view on the language of poetry. (M-07) (O-07)
Key to write answer:
Four types of misunderstanding:
o 1. Misunderstanding of the sense of poetry: Careless, intuitive reading (rhyme or irregular syntax)
o 2. Over-literal reading – prosaic reading
o 3. Defective scholarship
o 4. Difference in meaning of words in poetry and prose
Example: Solemn and gray…
Explain with the example of - A health, a ringing health…..
v What are the dangers of over-literal examination of figurative language?
· Discuss three critics’ comment on Climb, cloud….
- What are Richards’s views on Personification?
- ………………………………visual memory?
- ……………………. Comparative criticism?
- Task 1: You shall analyse one poem from this list of 30 poems. You shall select the poem that matched with your roll number. You are free to mutually change the poem with your friends. If you are writing blog on the analysis that you want to discuss in the class, submit the blog link in the comment and in Google Classroom.
- Task 2: After classroom discussion, you are supposed to write a blog on 'verbal analysis' of the poem / song / film song lyric / hymns / devotional songs or any poetic expression in any language of your own choice. Keep in mind the kinds of misunderstanding discussed in the essay 'Figurative Language'. Based on the analysis given in the essay, give your comments on the poetic expression selected by you. Post the original work along with your comments on your personal blog. Share the link of this blog-post in the COMMENTS below this blog-post. In the comment, write an 'ABSTRACT' of your blog-post along with link of the post. Also submit the link of the blogpost in Google Classroom.
Thursday, 25 December 2008
Experimenting ICT in English Language and Literature
This article was published in 'The AsiaCall Online Journal (ISSN: 1936-9859). The full article can be downloaded from this link: Click here to Download full article.
We live in an era of information explosion. Once there was famine of information, today we are drowned in the deluge of information. Gale of change is blowing in the pedagogy of Teaching English Language and Literature (TELL). Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is a catalyst agent. ICT has initiated new possibilities into the classroom. The marriage between education and Internet technology has made a deep impact on perspectives about teaching and learning. The role of the teacher, the nature and context of learning, as well as the function and relative importance of course content have all been challenged and redefined. Technophobic teachers have no place in this new world order.
This paper aims at sharing practical experiments with ICT in Teaching English Language and Literature. It deals with pragmatic aspects of using ICT with the student community of Business Management and Humanities. The extensive use of web 2.0 components, internet, blogs, e-groups, SMSs, emails, socializing portals, e-dictionaries, e-ncyclopedia, ppt presentations, webcasting, audio-video etc as teaching tools were experimented in the classroom. The student community was motivated to make use of cyber cafes and GPRS mobiles to interact with the teacher.
The paper deals with very pertinent questions:
• How far is ICT useful to student community?
• What is the role of ICT in teaching English language and literature?
• What kind of methods can be used to overcome students' problems?
• Can it empower student community? Can it improve their proficiency of learning?
We live in an era of information explosion. Once there was famine of information, today we are drowned in the deluge of information. Gale of change is blowing in the pedagogy of Teaching English Language and Literature (TELL). Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is a catalyst agent. ICT has initiated new possibilities into the classroom. The marriage between education and Internet technology has made a deep impact on perspectives about teaching and learning. The role of the teacher, the nature and context of learning, as well as the function and relative importance of course content have all been challenged and redefined. Technophobic teachers have no place in this new world order.
This paper aims at sharing practical experiments with ICT in Teaching English Language and Literature. It deals with pragmatic aspects of using ICT with the student community of Business Management and Humanities. The extensive use of web 2.0 components, internet, blogs, e-groups, SMSs, emails, socializing portals, e-dictionaries, e-ncyclopedia, ppt presentations, webcasting, audio-video etc as teaching tools were experimented in the classroom. The student community was motivated to make use of cyber cafes and GPRS mobiles to interact with the teacher.
The paper deals with very pertinent questions:
• How far is ICT useful to student community?
• What is the role of ICT in teaching English language and literature?
• What kind of methods can be used to overcome students' problems?
• Can it empower student community? Can it improve their proficiency of learning?
How to cite this article:
APA
Barad, D. (2010). EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE. AsiaCALL Online Journal, 4(1). Retrieved 2010-07-04, from
MLA
Barad, Dilip. "EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE" AsiaCALL Online Journal [Online], 4 3 Jul 2010
CBE
Barad, D. 2010 Jul 3. EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE. AsiaCALL Online Journal. [Online] 4:1
ABNT
Barad, D.. EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE. AsiaCALL Online Journal, North America, 4 3 07 2010.
Bib Tex
@article{{ACOJ}{21},
author = {Barad, D.},
title = {EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE},
journal = {AsiaCALL Online Journal},
volume = {4},
number = {1},
year = {2010},
url = {http://asiacall.info/journals/asiacall_online/index.php/olj/article/view/21/16}
}
Ref Works
@article{{ACOJ}{21},
author = {Barad, D.},
title = {EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE},
journal = {AsiaCALL Online Journal},
volume = {4},
number = {1},
year = {2010},
url = {http://asiacall.info/journals/asiacall_online/index.php/olj/article/view/21/16}
}
Turabian
Barad, Dilip. "EXPERIMENTING ICT IN TEACHING ENGLISH LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE" AsiaCALL Online Journal [Online], Volume 4 Number 1 (3 July 2010)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)